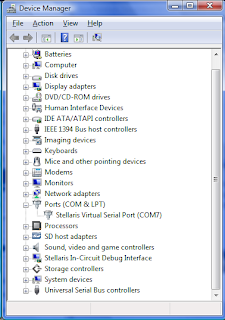
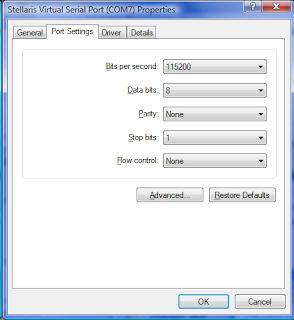
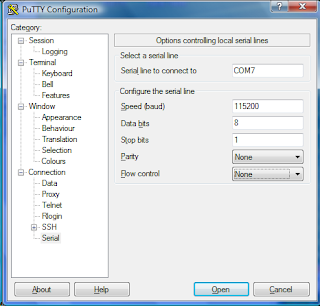
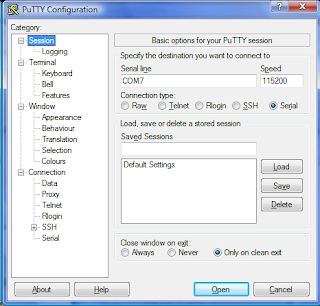
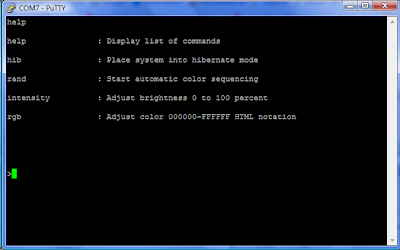
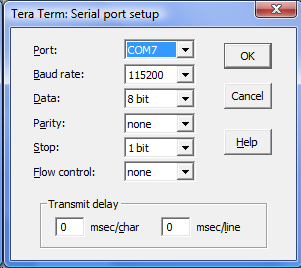
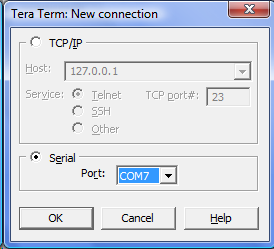
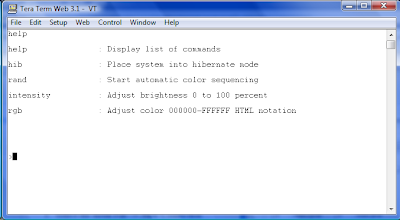
Abbreviation
(my name)
|
Code Example and Notes
|
2al (arrays as list) |
List<String>
list = new ArrayList<String>(
Arrays.asList(arr));
Note: replaces both String with the name
you type |
2ar (to array) |
clazz[]
arr = coll.toArray(new clazz[coll.size()]); |
2l (arrays as list) |
List<String>
list = Arrays.asList(arr); |
2s (double set) |
Set<String>
set = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(arr));
Note: replace both String with the word
you type |
En (enumeration) |
Enumeration|
|
Ex (exception) |
Exception|
|
Ob (object) |
Object| |
Pf (public final) |
public final | |
Pfm (public final method) |
public final void
method() {
} |
Pm (public method) |
public void
method() {
}
|
Ps (public static) |
public static | |
Psf (public static final) |
public static final | |
Psfb (public static final boolean) |
public static final boolean |
|
Psfi (public static final int)
|
public static final int | |
Psfm (public static final method) |
public static final void
method() {
} |
Psfs (private static final string) |
private static final String | |
St (string) |
String| |
ab (abstract) |
abstract | |
al (array list) |
List <String>
l = new ArrayList <String>();
Note: replaces both String with the name
you type |
ap (append) |
sb.append(); |
apo (append expression) |
if (sb.length()
> 0) {
sb.append (',');
}
sb.append ("exp=");
sb.append (exp);
|
as (assert) |
assert boolean; |
asort (array sort) |
Arrays.sort(Array);
|
bcom (block comment) |
/*|*/ |
bo (boolean) |
boolean | |
br (break) |
break;| |
ca (catch) |
catch (Exception
ex) {
} |
cl (class) |
class | |
cn (continue) |
continue| |
cs (case) |
case what:
break; |
csort (sort) |
Collections.sort(var); |
db (double) |
double | |
df (default) |
default:| |
do (do while block) |
do {
} while (boolean); |
dowhile (do while block) |
do {
} while (boolean); |
eq (equals) |
equals| |
ex (extends) |
extends | |
f (final) |
final | |
fa (false) |
false| |
fc (final class) |
final class Type {
Type() {
}
}
Note: replaces both Type with the name
you type |
fcom (edit fold for comment) |
//<editor-fold
defaultstate="collapsed" desc="comment">
//</editor-fold> |
fi (final) |
final | |
fl (float) |
float | |
for (old for block) |
for (int i
= 0; i < 10; i++) {
} |
forc (for iterator) |
for (Iterator it
= col.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
Object object = it.next();
} |
fore (new for each) |
for (Object object
: col) {
} |
forl (for block) |
for (int i = 0; i < lst.size(); i++) {
Object object = lst.get(i);
} |
form (for map block) |
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object>
entry
: m.entrySet()) {
Object object = entry.getKey();
Object object1 = entry.getValue();
}
Note: replaces all entry with the name
you type |
forst (for string tokenizer block) |
for (StringTokenizer stringTokenizer
=
new StringTokenizer(STRING);
stringTokenizer.hasMoreTokens();) {
String token =
stringTokenizer.nextToken();
}
Note: replaces all stringTokenizer names
with the name you type |
forv (for block) |
for (int i
= 0; i < vct.size(); i++) {
Object object = vct.elementAt(i);
} |
fy (finally block) |
finally {
|
} |
iae (illegal argument exception) |
throw new
IllegalArgumentException("arg"); |
ic (class) |
class Type
{
Type() {
}
}
Note: replace both Type with the name you
type |
ie (interface) |
interface | |
if (if block) |
if (boolean)
{
} |
ife (if else block) |
if (boolean)
{
} else {
} |
ifelse (if else block) |
if (boolean)
{
} else {
} |
iff (if statement) |
if (boolean)
{
} |
im (implements) |
implements | |
in (interface) |
interface | |
inst (instanceof test) |
if (instanceName
instanceof Object) {
Object object = (Object) sb;
}
|
iof (instanceof) |
instanceof | |
if (if statement) |
if (boolean)
{
} |
ise (illegal state exception) |
throw new IllegalStateException("arg");
|
jaxbm (jaxb marhaller) |
try {
javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext jaxbCtx =
javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext.newInstance(
sb.getClass().getPackage().getName());
javax.xml.bind.Marshaller marshaller =
jaxbCtx.createMarshaller();
marshaller.setProperty(javax.xml.bind.Marshaller.JAXB_ENCODING,
"UTF-8"); //NOI18N
marshaller.setProperty(
javax.xml.bind.Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT,
Boolean.TRUE);
marshaller.marshal(sb, System.out);
} catch (javax.xml.bind.JAXBException ex)
{
java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger("global")
.log(java.util.logging.Level.SEVERE,
null, ex);
}
Note: replaces both sb with the name you
type
|
jaxbu (jaxb unmarshaller) |
try {
javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext jaxbCtx =
javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext.newInstance(
sb.getClass().getPackage().getName());
javax.xml.bind.Unmarshaller unmarshaller
=
jaxbCtx.createUnmarshaller();
sb = (StringBuilder)
unmarshaller.unmarshal(
new java.io.File("File path"));
//NOI18N
} catch (javax.xml.bind.JAXBException ex)
{
java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger(
"global").log(java.util.logging.Level.SEVERE,
null, ex);
}
Note: replaces both sb with the name you
type |
le (length) |
length| |
ll (linked list) |
List<String>
list = new LinkedList<String>();
Note: replaces both String with the name
you type |
logb (log bundle key) |
logger.log(Level.INFO,
"bundle_key"); |
logbps (log bundle key with format) |
logger.log(Level.INFO,
"bundle_key", new Object[]{null}); |
logr (logger) |
private static final Logger logger =
Logger.getLogger(CurrentClass.class.getName());| |
logrb (logger) |
private static final Logger logger =
Logger.getLogger(CurrentClass.class.getName(),
CurrentClass.class.getPackage().getName() + ".Log"); |
m (new method) |
private
static final void method() {
} |
map (map) |
Map<String,
String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); |
n (new object) |
Object
object = new Object();
Note: replace all three object with the
name you type while keeping the camel case on object; i.e.:
newo MyObject
MyObject myObject = new MyObject(); |
na (native) |
native | |
newo (new object) |
Object
object = new Object();
Note: replace all three object with the
name you type while keeping the camel case on object; i.e.:
newo MyObject
MyObject myObject = new MyObject(); |
npe (null pointer exception) |
throw new NullPointerException("sb"); |
pe (protected) |
protected | |
pf (private final) |
private final | |
pfc (private final class) |
private final class Type
{
Type() {
}
}
Note: replaces both Type with the name
you type |
pfm (private final method) |
private final void
method() {
} |
pm (private method) |
private void
method() {
} |
pr (private) |
private | |
prfm (protected final method) |
protected final void
method() {
} |
prm (protected method) |
protected void
method() {
} |
prsfm (protected static final method) |
protected static final void
method() {
} |
ps (private static) |
private static | |
psf (private static final) |
private static final | |
psfb (private static final boolean) |
private static final boolean | |
psfc (private static final class) |
private static final class Type
{
Type() {
}
}
Note: replaces both Type with the word
you type |
psfi (private static final int) |
private static final int | |
psfs (private static final string) |
private static final String | |
psm (private static method) |
private static void
method() {
} |
pst (print stack trace) |
printStackTrace();| |
psvm (main method) |
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
} |
pu (public) |
public | |
pue (public enum) |
public enum Type
{
} |
pvb (private volatile boolean) |
private volatile boolean | |
re (return) |
return |
|
rn (return null) |
return null;| |
runn (runnable) |
Runnable runnable
= new Runnable() {
public void run() {
}
};
|
sb (string builder) |
StringBuilder stringBuilder
= new StringBuilder(); |
sc (static class) |
static class Type
{
Type() {
}
}
Note: Replaces both Type with the name
you type |
serr (system error) |
System.err.println("|"); |
set (new hashset) |
Set<String>
set = new HashSet<String>();
Note: Replaces both String with the word
you type |
sfc (static final class) |
static final class Type
{
Type() {
}
Note: Replaces both Type with the name
you type |
sh (short) |
short | |
sout (system out) |
System.out.println("|"); |
soutv (system out with text) |
System.out.println("sb
= " + sb); |
spl (for string.split) |
for (String string
: string.split(",")) {
} |
st (static) |
static | |
su (super) |
super|
|
sw (switch statement) |
switch (var)
{
case val:
break;
default:
throw new AssertionError();
}
|
sy (synchronized) |
synchronized | |
tds (thread dump stack) |
Thread.dumpStack();| |
th (throws) |
throws |
|
tr (transient) |
transient | |
trycatch (try-catch block) |
try {
|
} catch (Exception e) {
} |
tw (throw with excpetion) |
throw
new IllegalStateException();
|
vo (volatile) |
volatile | |
wh (while) |
while (boolean)
{
}
Notes: attempts to find boolean |
whileit (while with iterator) |
while (it.hasNext())
{
Object object = it.next();
}
Notes: attempts to find an iterator |
whilen (while with enumerator) |
while (en.hasMoreElements())
{
Object object = en.nextElement();
}
Notes: attempts to find an enumerator |
whilexp (while with expression) |
while (boolean)
{
}
Notes: attempts to find a boolean value |